- Rhino Mac Line Weights Sheet
- Drafting Line Weights
- Rhino Mac Line Weights Tool
- Rhino Head Weight
- Rhino Mac Line Weights Sheet
- Rhino Mac Line Weights For Beginners
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| AngularDimension | Represents a dimension of an entity that can be measured with an angle. This entity refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| AnnotationBase | Provides a common base class to all annotation geometry. This class refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| ArcCurve | Represent arcs and circles. ArcCurve.IsCircle returns true if the curve is a complete circle. |
| AreaMassProperties | Contains static initialization methods and allows access to the computed metrics of area, area centroid and area moments in closed planar curves, in meshes, in surfaces, in hatches and in boundary representations. |
| BezierCurve | Represents a Bezier curve. Note: as an exception, the bezier curve is not derived from Curve. |
| Brep | Boundary Representation. A surface or polysurface along with trim curve information. |
| BrepEdge | Represents a single edge curve in a Brep object. |
| BrepFace | Provides strongly-typed access to brep faces. A Brep face is composed of one surface and trimming curves. |
| BrepLoop | Represent a single loop in a Brep object. A loop is composed of a list of trim curves. |
| BrepRegion | Represents a brep topological region that has sides. |
| BrepRegionFaceSide | |
| BrepTrim | Brep trim information is stored in BrepTrim classes. Brep.Trims is an array of all the trims in the brep. A BrepTrim is derived from CurveProxy so the trim can supply easy to use evaluation tools via the Curve virtual member functions. Note well that the domains and orientations of the curve m_C2[trim.m_c2i] and the trim as a curve may not agree. |
| BrepVertex | |
| ClippingPlaneSurface | Represents a planar surface that is used as clipping plane in viewports. |
| Curve | Represents a base class that is common to most RhinoCommon curve types. A curve represents an entity that can be all visited by providing a single parameter, usually called t. |
| CurveProxy | |
| DetailView | Represents a view of the model placed on a page layout. |
| Extrusion | Represents an extrusion, or objects such as beams or linearly extruded elements, that can be represented by profile curves and two miter planes at the extremes. |
| GeometryBase | Provides a common base for most geometric classes. This class is abstract. |
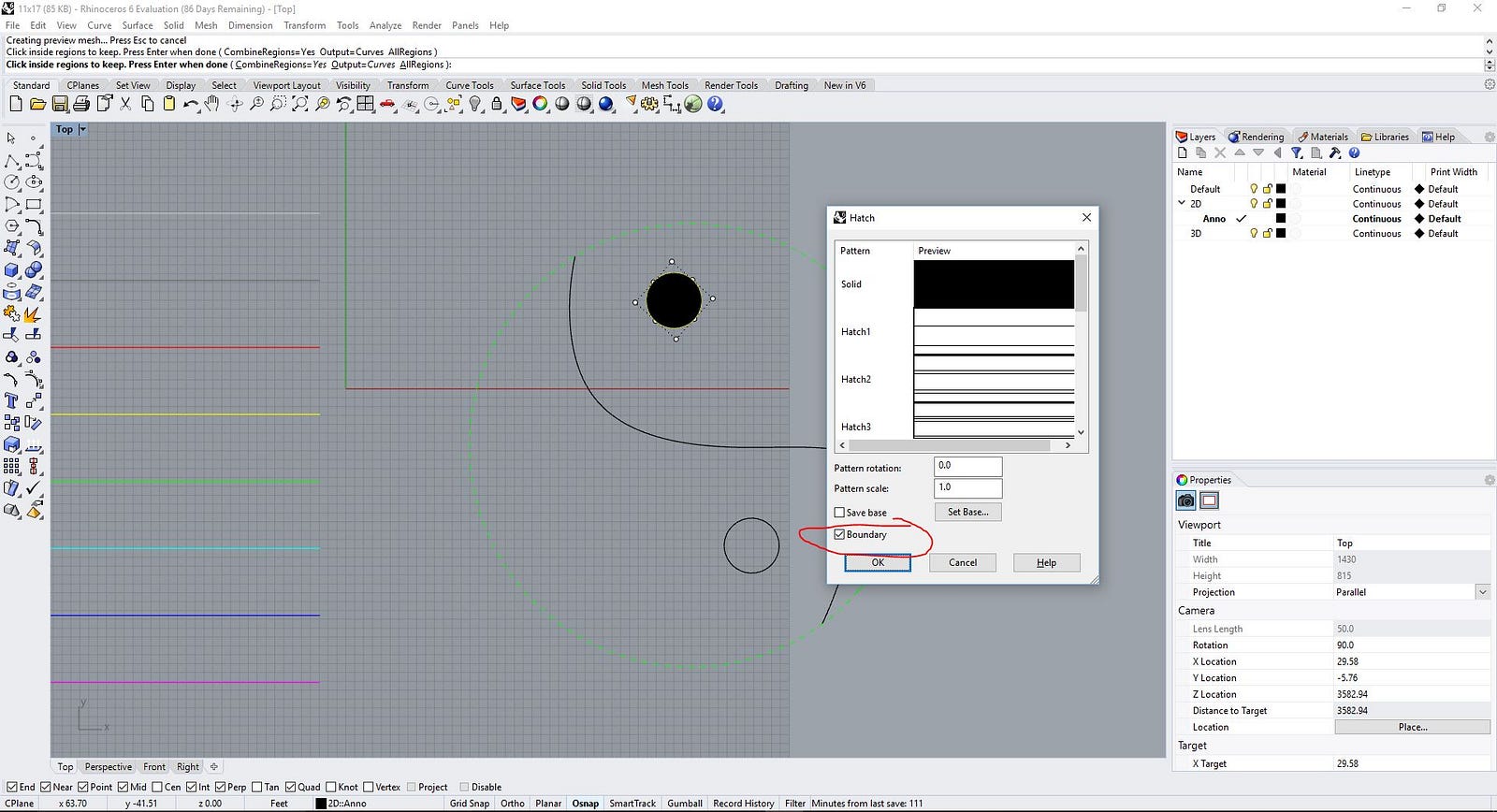
| Hatch | Represents a hatch in planar boundary loop or loops. This is a 2d entity with a plane defining a local coordinate system. The loops, patterns, angles, etc are all in this local coordinate system. The Hatch object manages the plane and loop array Fill definitions are in the HatchPattern or class derived from HatchPattern Hatch has an index to get the pattern definition from the pattern table. |
| InstanceDefinitionGeometry | |
| InstanceReferenceGeometry | Represents a reference to the geometry in a block definition. |
| Interpolator | Exposes a set of standard numeric interpolation algorithms. |
| Leader | Represents a leader, or an annotation entity with text that resembles an arrow pointing to something. This class refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| Light | Represents a light that shines in the modeling space. |
| LinearDimension | Represents a linear dimension. This entity refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| LineCurve | |
| Matrix | Represents an arbitrarily sized matrix of double-precision floating point numbers. If you are working with a 4x4 matrix, then you may want to use the Transform class instead. |
| Mesh | Represents a geometry type that is defined by vertices and faces. This is often called a face-vertex mesh. |
| MeshingParameters | Represents settings used for creating a mesh representation of a brep or surface. |
| MeshPart | |
| MeshPoint | Represents a point that is found on a mesh. |
| MorphControl | Represents a geometry that is able to control the morphing behaviour of some other geometry. |
| NurbsCurve | Represents a Non Uniform Rational B-Splines (NURBS) curve. |
| NurbsSurface | Represents a Non Uniform Rational B-Splines (NURBS) surface. |
| OrdinateDimension | Represents the geometry of a dimension that displays a coordinate of a point. This class refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| Particle | Represents a simple particle. This base class only defines position and display properties (size, color, bitmap id). You will most likely create a class that derives from this particle class to perform some sort of physical simulation (movement over time or frames). |
| ParticleSystem | |
| PlaneSurface | Represents a plane surface, with plane and two intervals. |
| Point | Represents a geometric point. This is fundamentally a class that derives from GeometryBase and contains a single Point3d location. |
| Point3dGrid | |
| PointCloud | Represents a collection of coordinates with optional normal vectors and colors. |
| PointCloudItem | Represents a single item in a pointcloud. A PointCloud item always has a location, but it has an optional normal vector and color. |
| PolyCurve | Represents a curve that is the result of joining several (possibly different) types of curves. |
| Polyline | Represents an ordered set of points connected by linear segments. Polylines are closed if start and end points coincide. |
| PolylineCurve | Represents the geometry of a set of linked line segments. This is fundamentally a class that derives from Curve and internally contains a Polyline. |
| RadialDimension | Represents a dimension of a circular entity that can be measured with radius or diameter. Mr. macs virtual existencegrade 9 health. This entity refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| RevSurface | Represents a surface of revolution. Revolutions can be incomplete (they can form arcs). |
| RTree | Represents a spatial search structure based on implementations of the R-tree algorithm by Toni Gutman. |
| RTreeEventArgs | Represents event data that is passed when when an item that meets certain criteria is found and the passed RTree event is raised. |
| SpaceMorph | |
| SumSurface | Represents a sum surface, or an extrusion of a curve along a curved path. |
| Surface | Represents a base class that is common to most RhinoCommon surface types. A surface represents an entity that can be all visited by providing two independent parameters, usually called (u, v), or sometimes (s, t). |
| SurfaceCurvature | Maintains computed information for surface curvature evaluation. |
| SurfaceProxy | Provides a base class to brep faces and other surface proxies. |
| SweepOneRail | Utility class for generating breps by sweeping cross section curves over a single rail curve. |
| SweepTwoRail | Utility class for generating breps by sweeping cross section curves over two rail curves. |
| TextDot | Represents a text dot, or an annotation entity with text that always faces the camera and always has the same size. This class refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| TextEntity | Represents text geometry. This class refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| Unroller | Represents the operation of unrolling a single surface. |
| VolumeMassProperties | Contains static initialization methods and allows access to the computed metrics of volume, volume centroid and volume moments in in solid meshes, in solid surfaces and in solid (closed) boundary representations. |


- Rhino Mac Line Weights Sheet
- Drafting Line Weights
- Rhino Mac Line Weights Tool
- Rhino Head Weight
- Rhino Mac Line Weights Sheet
- Rhino Mac Line Weights For Beginners
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| AngularDimension | Represents a dimension of an entity that can be measured with an angle. This entity refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| AnnotationBase | Provides a common base class to all annotation geometry. This class refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| ArcCurve | Represent arcs and circles. ArcCurve.IsCircle returns true if the curve is a complete circle. |
| AreaMassProperties | Contains static initialization methods and allows access to the computed metrics of area, area centroid and area moments in closed planar curves, in meshes, in surfaces, in hatches and in boundary representations. |
| BezierCurve | Represents a Bezier curve. Note: as an exception, the bezier curve is not derived from Curve. |
| Brep | Boundary Representation. A surface or polysurface along with trim curve information. |
| BrepEdge | Represents a single edge curve in a Brep object. |
| BrepFace | Provides strongly-typed access to brep faces. A Brep face is composed of one surface and trimming curves. |
| BrepLoop | Represent a single loop in a Brep object. A loop is composed of a list of trim curves. |
| BrepRegion | Represents a brep topological region that has sides. |
| BrepRegionFaceSide | |
| BrepTrim | Brep trim information is stored in BrepTrim classes. Brep.Trims is an array of all the trims in the brep. A BrepTrim is derived from CurveProxy so the trim can supply easy to use evaluation tools via the Curve virtual member functions. Note well that the domains and orientations of the curve m_C2[trim.m_c2i] and the trim as a curve may not agree. |
| BrepVertex | |
| ClippingPlaneSurface | Represents a planar surface that is used as clipping plane in viewports. |
| Curve | Represents a base class that is common to most RhinoCommon curve types. A curve represents an entity that can be all visited by providing a single parameter, usually called t. |
| CurveProxy | |
| DetailView | Represents a view of the model placed on a page layout. |
| Extrusion | Represents an extrusion, or objects such as beams or linearly extruded elements, that can be represented by profile curves and two miter planes at the extremes. |
| GeometryBase | Provides a common base for most geometric classes. This class is abstract. |
| Hatch | Represents a hatch in planar boundary loop or loops. This is a 2d entity with a plane defining a local coordinate system. The loops, patterns, angles, etc are all in this local coordinate system. The Hatch object manages the plane and loop array Fill definitions are in the HatchPattern or class derived from HatchPattern Hatch has an index to get the pattern definition from the pattern table. |
| InstanceDefinitionGeometry | |
| InstanceReferenceGeometry | Represents a reference to the geometry in a block definition. |
| Interpolator | Exposes a set of standard numeric interpolation algorithms. |
| Leader | Represents a leader, or an annotation entity with text that resembles an arrow pointing to something. This class refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| Light | Represents a light that shines in the modeling space. |
| LinearDimension | Represents a linear dimension. This entity refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| LineCurve | |
| Matrix | Represents an arbitrarily sized matrix of double-precision floating point numbers. If you are working with a 4x4 matrix, then you may want to use the Transform class instead. |
| Mesh | Represents a geometry type that is defined by vertices and faces. This is often called a face-vertex mesh. |
| MeshingParameters | Represents settings used for creating a mesh representation of a brep or surface. |
| MeshPart | |
| MeshPoint | Represents a point that is found on a mesh. |
| MorphControl | Represents a geometry that is able to control the morphing behaviour of some other geometry. |
| NurbsCurve | Represents a Non Uniform Rational B-Splines (NURBS) curve. |
| NurbsSurface | Represents a Non Uniform Rational B-Splines (NURBS) surface. |
| OrdinateDimension | Represents the geometry of a dimension that displays a coordinate of a point. This class refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| Particle | Represents a simple particle. This base class only defines position and display properties (size, color, bitmap id). You will most likely create a class that derives from this particle class to perform some sort of physical simulation (movement over time or frames). |
| ParticleSystem | |
| PlaneSurface | Represents a plane surface, with plane and two intervals. |
| Point | Represents a geometric point. This is fundamentally a class that derives from GeometryBase and contains a single Point3d location. |
| Point3dGrid | |
| PointCloud | Represents a collection of coordinates with optional normal vectors and colors. |
| PointCloudItem | Represents a single item in a pointcloud. A PointCloud item always has a location, but it has an optional normal vector and color. |
| PolyCurve | Represents a curve that is the result of joining several (possibly different) types of curves. |
| Polyline | Represents an ordered set of points connected by linear segments. Polylines are closed if start and end points coincide. |
| PolylineCurve | Represents the geometry of a set of linked line segments. This is fundamentally a class that derives from Curve and internally contains a Polyline. |
| RadialDimension | Represents a dimension of a circular entity that can be measured with radius or diameter. Mr. macs virtual existencegrade 9 health. This entity refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| RevSurface | Represents a surface of revolution. Revolutions can be incomplete (they can form arcs). |
| RTree | Represents a spatial search structure based on implementations of the R-tree algorithm by Toni Gutman. |
| RTreeEventArgs | Represents event data that is passed when when an item that meets certain criteria is found and the passed RTree event is raised. |
| SpaceMorph | |
| SumSurface | Represents a sum surface, or an extrusion of a curve along a curved path. |
| Surface | Represents a base class that is common to most RhinoCommon surface types. A surface represents an entity that can be all visited by providing two independent parameters, usually called (u, v), or sometimes (s, t). |
| SurfaceCurvature | Maintains computed information for surface curvature evaluation. |
| SurfaceProxy | Provides a base class to brep faces and other surface proxies. |
| SweepOneRail | Utility class for generating breps by sweeping cross section curves over a single rail curve. |
| SweepTwoRail | Utility class for generating breps by sweeping cross section curves over two rail curves. |
| TextDot | Represents a text dot, or an annotation entity with text that always faces the camera and always has the same size. This class refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| TextEntity | Represents text geometry. This class refers to the geometric element that is independent from the document. |
| Unroller | Represents the operation of unrolling a single surface. |
| VolumeMassProperties | Contains static initialization methods and allows access to the computed metrics of volume, volume centroid and volume moments in in solid meshes, in solid surfaces and in solid (closed) boundary representations. |
What Is MAC?
File I/O - File doesn't open on Mac. Make2D: Text affects Make2d scale. PrintPreview: PrintDisplay and Default line weight (RH-56294 1) SDK: Unexpected issues with deleting Display Modes. SDK: RhinoCommon: Added BrepEdgeList.MergeEdge and BrepEdgeList.MergeAllEdges. Ways to improve line weight in traditional media sketches. New Gumroad tutorials going live now, https://gumroad.com/l/LXPY.
Rhino Mac Line Weights Sheet
Mycobacterium Avium Complex (MAC) is a serious illness caused by common bacteria. MAC is also known as MAI (Mycobacterium Avium Intracellulare). MAC infection can be localized (limited to one part of your body) or disseminated (spread through your whole body, sometimes called DMAC). MAC infection often occurs in the lungs, intestines, bone marrow, liver and spleen. Snip tool for mac free.
The bacteria that cause MAC are very common. They are found in water, soil, dust and food. Almost everyone has them in their body. A healthy immune system will control MAC, but people with weakened immune systems can develop MAC disease.
Up to 50% of people with AIDS may develop MAC, especially if their CD4 cell count is below 50. MAC almost never causes disease in people with more than 100 CD4 cells.
How Do I Know if I Have MAC?
The symptoms of MAC can include high fevers, chills, diarrhea, weight loss, stomach aches, fatigue, and anemia (low numbers of red blood cells). When MAC spreads in the body, it can cause blood infections, hepatitis, pneumonia, and other serious problems.
Drafting Line Weights
Many different opportunistic infections can cause these symptoms. Therefore, your health care provider will probably check your blood, urine, or saliva to look for the bacteria that causes MAC. The sample will be tested to see what bacteria are growing in it. This process, called culturing, can take several weeks. Even if you are infected with MAC, it can be hard to find the MAC bacteria.
If your CD4 cell count is less than 50, your health care provider might treat you for MAC, even without a definite diagnosis. This is because MAC infection is very common but can be difficult to diagnose.
How Is MAC Treated?
The MAC bacteria can mutate and develop resistance to some of the drugs used to fight it. Health care providers use a combination of antibacterial drugs (antibiotics) to treat MAC. At least two drugs are used: usually azithromycin or clarithromycin plus up to three other drugs. MAC treatment must continue for life, or else the disease will return.
People react differently to anti-MAC drugs. You and your health care provider may have to try different combinations before you find one that works for you with the fewest side effects.
The most common MAC drugs and their side effects are:
- Amikacin (Amkin®): kidney and ear problems; taken as an injection.
- Azithromycin (Zithromax®, see Fact Sheet 530): nausea, headaches, vomiting, diarrhea; taken as capsules or intravenously.
- Ciprofloxacin (Cipro® or Ciloxan®, see Fact Sheet 531): nausea, vomiting, diarrhea; taken as tablets or intravenously.
- Clarithromycin (Biaxin®, see Fact Sheet 532): nausea, headaches, vomiting, diarrhea; taken as capsules or intravenously. Note: The maximum dose is 500 milligrams twice a day.
- Ethambutol (Myambutol®): nausea, vomiting, vision problems.
- Rifabutin (Mycobutin®): rashes, nausea, anemia. Many drug interactions.
- Rifampin (Rifampicin®, Rifadin®, Rimactane®): fever, chills, muscle or bone pain; can turn urine, sweat, and saliva red-orange (may stain contact lenses); can interfere with birth control pills. Many drug interactions.
Can MAC Be Prevented?
The bacteria that cause MAC are very common. It is not possible to avoid being exposed. The best way to prevent MAC is to take strong antiretroviral medications (ARVs). Even if your CD4 cell count drops very low, there are drugs that can stop MAC disease from developing in up to 50% of people.
Rhino Mac Line Weights Tool
The antibiotic drugs azithromycin, rifabutin and clarithromycin have been used to prevent MAC. These drugs are usually prescribed for people with less than 50 CD4 cells.
Combination antiretroviral therapy can make your CD4 cell count go up. If it goes over 100 and stays there for 3 months, it may be safe to stop taking medications to prevent MAC. Be sure to talk with your health care provider before you stop taking any of your prescribed medications.
Drug Interaction Problems
Several drugs used to treat MAC interact with many other drugs, including ARVs, antifungal drugs, and birth control pills. This is especially true for rifampin, rifabutin, and rifapentine. Be sure your health care provider knows about all the medications that you are taking so that all possible interactions can be considered.
The Bottom Line
Rhino Head Weight
MAC is a serious disease caused by common bacteria. MAC can cause serious weight loss, diarrhea, and other symptoms.
Rhino Mac Line Weights Sheet
If you develop MAC, you will probably be treated with azithromycin or clarithromycin plus one to three other antibiotics. You will have to continue taking these drugs for life to avoid a recurrence of MAC.
Rhino Mac Line Weights For Beginners
People with 50 CD4 cells or less should talk with their health care providers about taking drugs to prevent MAC.
